The digital transformation in the economy has brought in technology advancement, but at the same time it has introduced new risks and financial frauds. Some of the instances of financial frauds such as fake transaction reversal, phishing, identity theft, money laundering, cybercrime and data fraud are increasing every day.
According to the recent KPMG’s Global Banking Fraud Survey report conducted across 43 retail banks, over half of respondents recover less than 25% of fraud losses; demonstrating that fraud prevention is key.
The complexity of fraud risks is increasing and needs to be effectively controlled through effective operational risk management processes as well as the use of fraud control security tools and processes.
Who’s Affected and How?
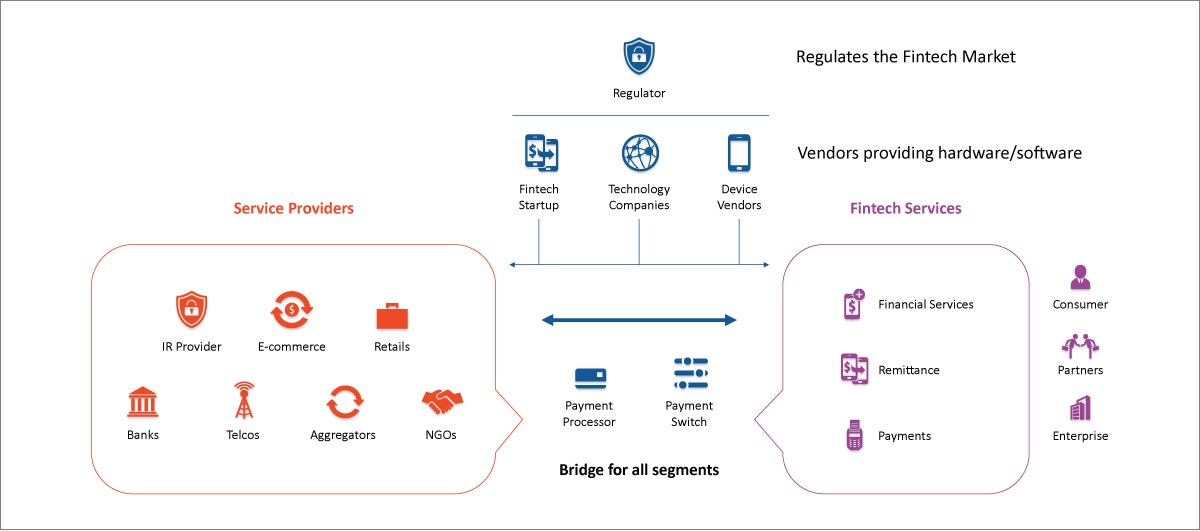
A financial service revolves around these main players in the ecosystem: Consumers, Agents/Partners, Enterprises, Regulators, and Service Providers. Let us understand how they are connected:
A financial service revolves around these main players in the ecosystem: Consumers, Agents/Partners, Enterprises, Regulators, and Service Providers. Let us understand how they are connected:
Any player in the ecosystem can be a victim of financial fraud by any other player. Frauds can happen at any phase of the engagement journey with the service provider (Acquisition, Transactional and Value addition).
The scenarios below describe some of the best examples of the types of frauds from the victim’s perspective, how each player can be a victim of the other ecosystem players, and how these frauds can be mitigated using an effective fraud management system.
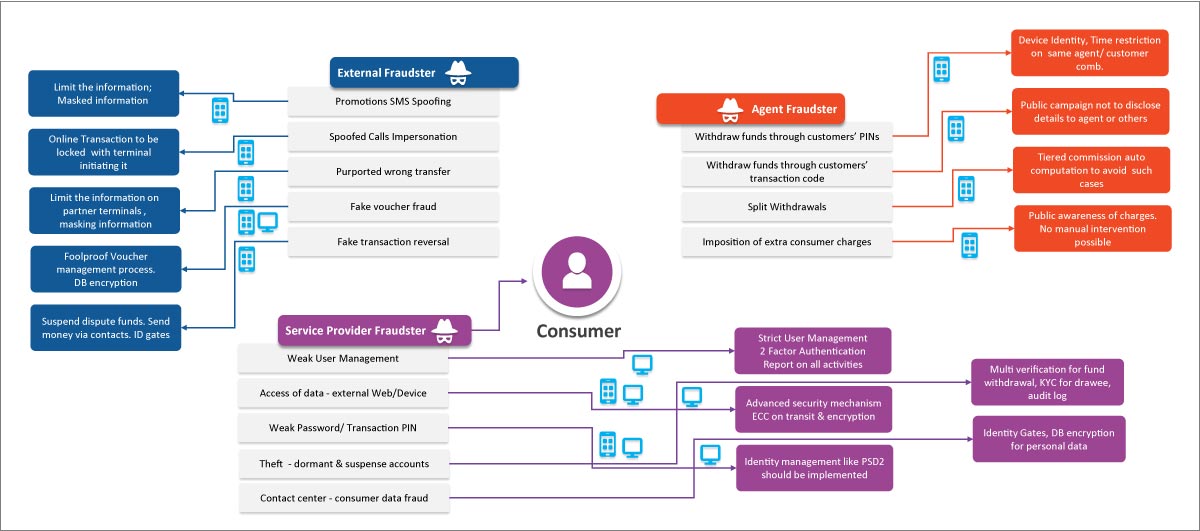
Consumer Frauds
Consumers are likely to be affected by external fraudsters through phishing and spoofing practices, agent fraudsters through transactions related frauds, and service fraudsters through consumer data malpractices. These can be mitigated by using secured technologies and tools as described for each of these fraud types below.
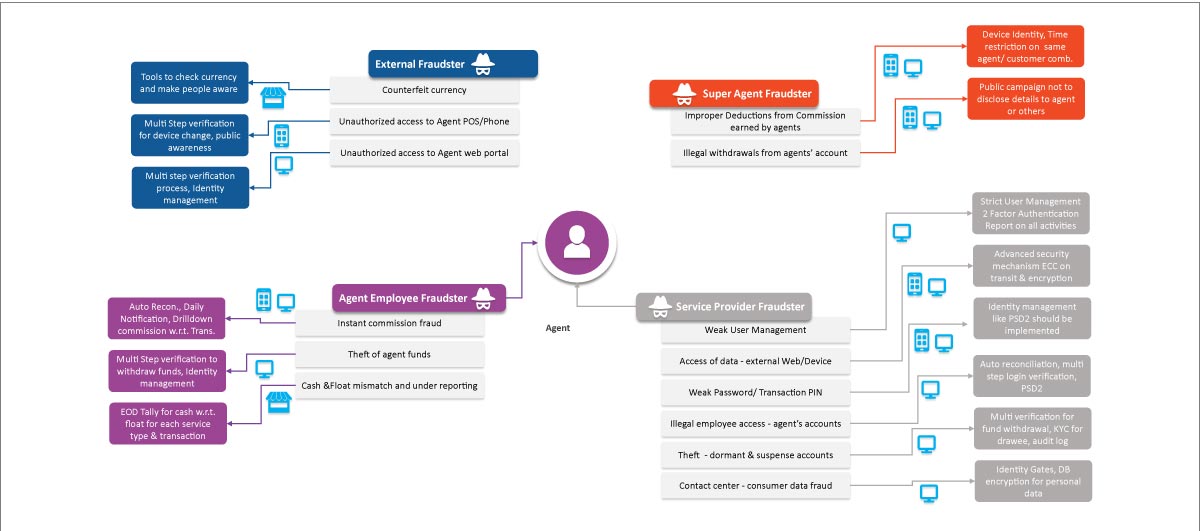
Agent Fraud or Partner Fraud
Super agents, agent employees, and service providers can also become perpetrators who commit financial frauds with an agent or partner through a variety of methods. These can be as simple as unauthorized access to agent phone or portal, to illegally withdrawing money from agent’s account, an instant commission fraud, or even an identity theft. However, these can be minimized if agents or partners have a mitigation plan as describe below for every type of fraud.
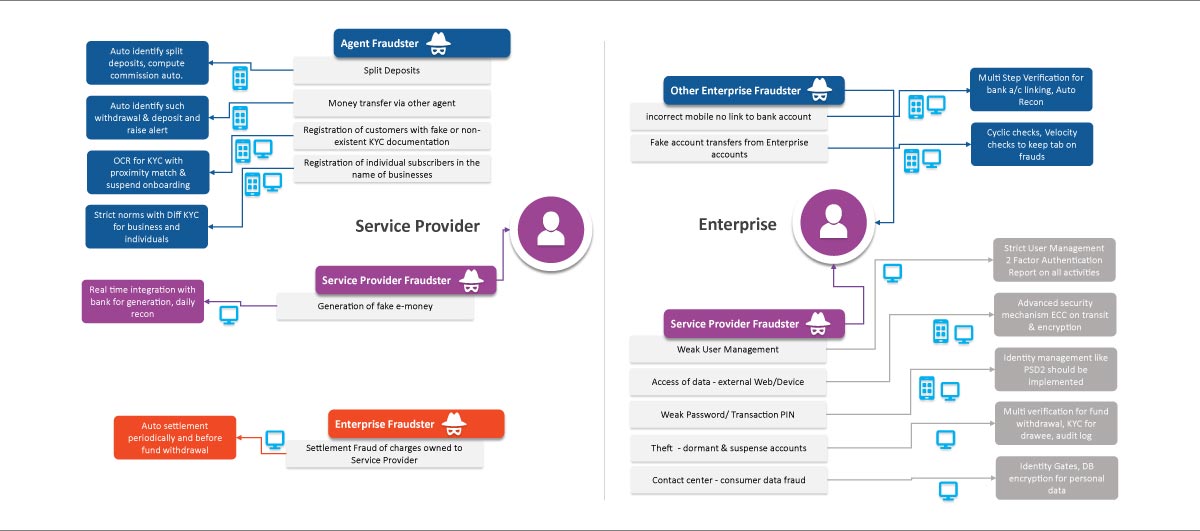
System Fraud or Service Provider Fraud
Service providers are open to financial risks from agents, enterprises, or other service providers such as split deposits, fake e-money, and so on.
To identify potentially fraudulent transactions, or access, service providers and enterprises need a proper mitigation plan and implement fraud prevention tools. Here are some of the most common frauds that victimize these players and their mitigation plan.
Using Technology to Mitigate Fraud Risk
As financial transactions increasingly rely on technology, they are becoming weapons of choice for the fraudsters, such as telecom fraud. However, the technology at the same time is helping victims to implement tools to remain secured. According to a global fraud report, 75% of businesses mentioned that they would be very interested in more advanced security measures and authentication."
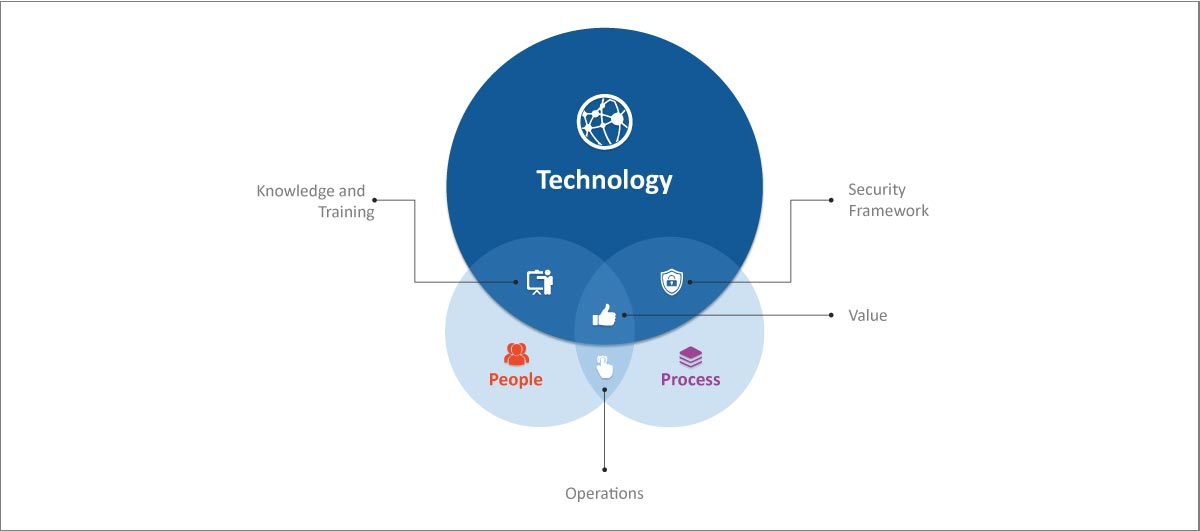
The magic potion for fraud management and mitigation will always be in the confluence of technology, processes and people to optimize operations.
Here’s how to stay afloat in the sea of technology frauds with secured fraud management practices and tools.
- Elliptic Curve Cryptography – an approach to asymmetric and symmetric key cryptography system, mostly for enterprise telecom fraud management. It is one of the most secured cryptography approaches to ensure financial security for data and transactions. Key examples include Bitcoin and MobiFin Elite.
- Strong PSD2 Compliance – the second Directive on Payment Services (PSD2) ensures that electronic payments are made with multi-factor authentication (for data with open APIs) that facilitates the security of payments and better use experience. This enables secured online transactions of consumer data with banks or third parties.
- Device Authentication – enables multi-factor authentication through push notifications, one-time passwords, SMS, email or more. OAuth 2.0 authentication, a multi-factor API authentication, is a mechanism for user authentication that allows secured payment processing.
- Secure Web Access - OWASP improves application security to minimize web risks or frauds. It provides security against injection flaws, broken authentication, sensitive data exposure, broken access control, insufficient logging and monitoring, and more.
- Velocity Checks –is a predictive fraud assessment technique to assess even before the fraud can occur. This is used to track velocity triggers and the number of transactions the fraudster has attempted in a given timeframe from a particular IP address, email address, phone, credit card number, and so on.
Conclusion
Financial and telecom fraud risk has increased as perpetrators use advanced technologies to identify and exploit weaknesses in financial systems, databases, and payment channels. You must ensure that a secured system is in place and necessary security measures are taken to prevent fraud. A strong fraud management system will certainly offer you a roadmap to identify, analyze, and prevent fraud regardless of its origin. If you think you can be a victim of any financial fraud, get on the road to mitigation plan with the right technology solution.
Contributing Writer: Neha is a digital marketing evangelist with over a decade of marketing experience and currently overlooks the entire inbound marketing activities and manages the team. Connect with her on Linkedin.