From the very beginning of the banking era, banks have offered various services like handling cash, providing credits, and other financial transactions. They also offer various physical branches to store cash and credit. Over a period of time, the banking industry introduced technology in an attempt to go digital and offer banking services online. With the effect of the COVID Pandemic, this attempt as now become a necessity. Social Distancing becoming a norm, it is required for banks to treat this urgency and offer their customers online services, thus making it convenient for them.
Neobank is one of the emerging trends in the digital banking platform space which is slowly changing the banking landscape.
To give a few examples of Neobanks, in 2018, Open announced its partnership with ICICI Bank which aimed to help businesses by integrating banking functions like sending invoices, payment collection, funds transfer, reconciliation, expense management – all from a single platform. The US has some of the oldest Neobanks like Simple (founded in 2009) and Moven (founded in 2011). There are also several new ones such as Chime, Varo, and Aspirations.
As per a recent Global Fintech adoption survey 2019. Fintech related financial services have 64% global consumer adoption. 96% of the global consumers are informed about at least one money transfer and payment fintech service. The top reasons for the increased adoption of Fintech services are the attractive rates and fees leading to 33% consumer adopters turning away from their main bank. The report states that 68% of the consumers would consider fintech companies for financial services. An interesting data suggests 46% of the consumer adopters are willing to share the bank data with other organizations.
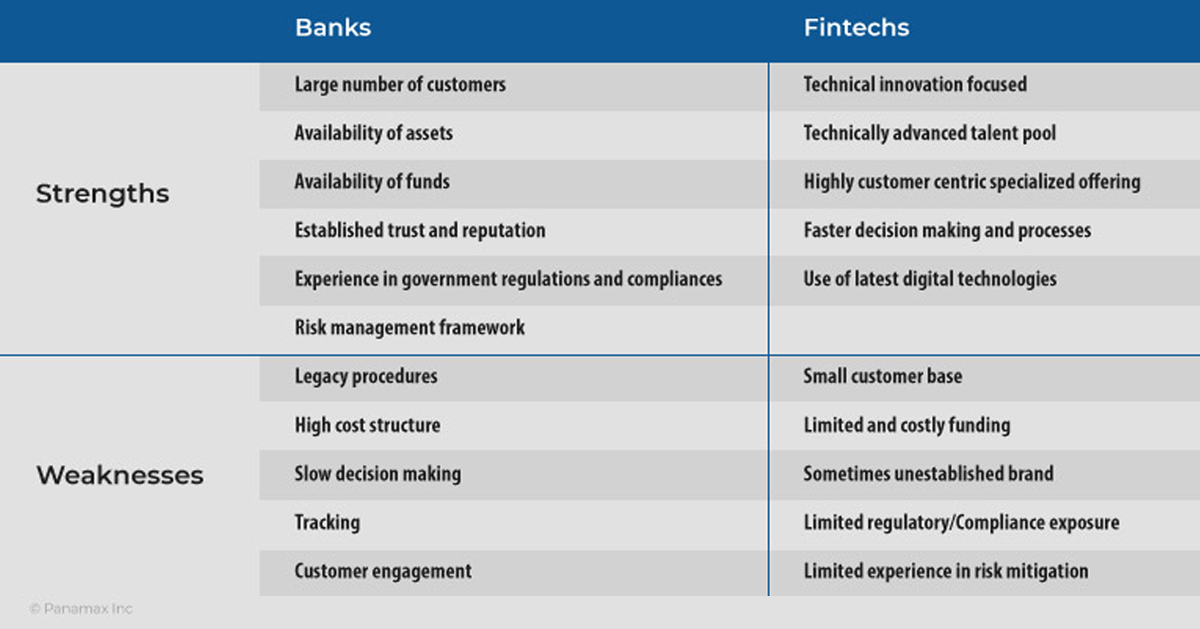
The Need for Partnership between Banks & Fintech
There exists a need for a handshake model between Fintech and banks. As per the Medici Report, Neobanks – A global deep dive Emerging markets are leading the way with an adoption rate of 87% in China and India. Russia and South Africa are close with 82% adoption. Few European countries like the Netherlands, the UK, and Ireland lead in adoption, signaling the development of open banking in the region. Indicatively, from the Medici Survey report, the adoption rate for six markets — Australia, Canada, Hong Kong, Singapore, the UK, and the US — has surged from 16% in 2015 to 31% in 2017 and 60% in 2019. Fintechs are becoming partners with the banks and bringing in latest technologies in the banking domain. With the increase of different services offered in the digital financial solutions domain, customer experience, and convenience has been the top priority and focus.
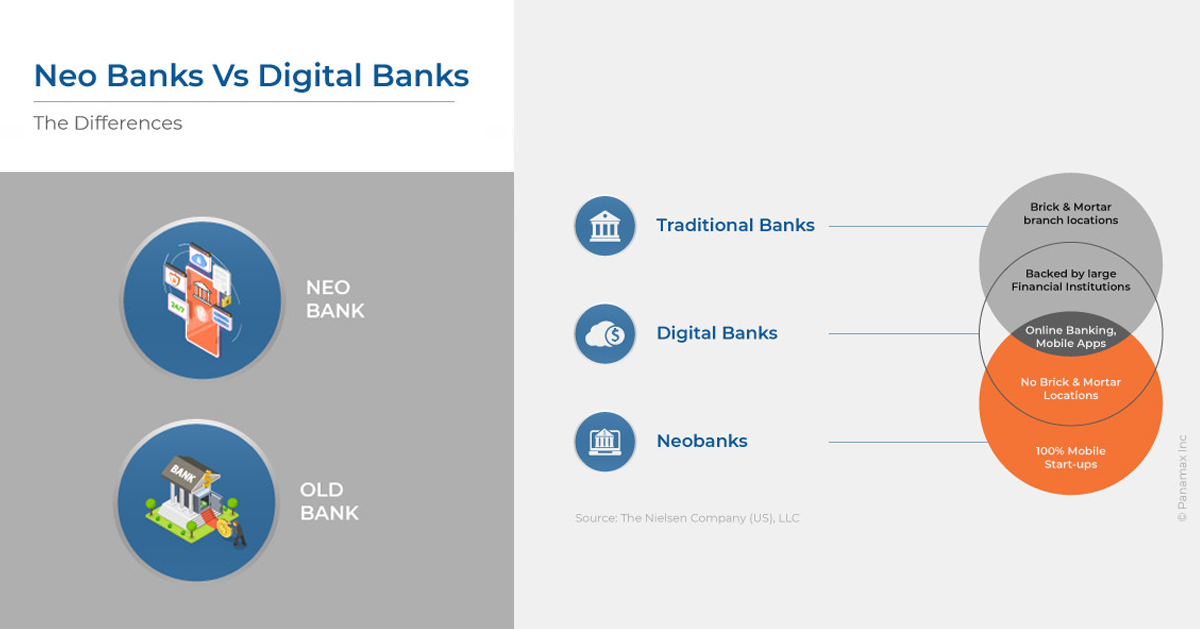
What is Neobank?
Neobank can be considered as a virtual bank that does not have any branches. It provides all traditional banking services on a mobile phone or a desktop device. It can be operated entirely online providing a seamless customer experience with new flavors of use cases. With this, there can be a wide range of banking as well as other financial services offered to the users.
Use Cases Offered by Neobanks
Neobanks offer a complete virtual experience in almost all domains of Fintech based on the business model and availability of infrastructure like:
- Microcredit/Emergency Loans/Mortgages/Home Loans/Auto Loans
- Insurances
- Different types of bank Accounts like Fixed Account/Joint Accounts/Corporate Account/Community Savings
- APIs for Open Banking
- Peer to Peer payments
- Virtual Cards (Debit Card/Credit Card/Global Cards)
- Marketplace (Lending, Crowdfunding, Trading)
- Loyalty Programs and Rewards
- Utility Payments/Bookings
- E-commerce
- Domestic and International Remittance
- Budget tracker/Smart Wealth Management
- Micro savings
Establishing a Neobank
Based on the availability of resources and required legality, Neobanks can be established under different business models:
Virtual Banking License
Many countries including Hongkong, South Korea, United States and, United Kingdom have already approved virtual banking licenses for Neobanks. With the virtual banking license, an organization can offer online banking services. While several other countries are still in the process of defining policies. It also enables them to have an improved core banking platform that allows smoother integration with external service providers they may choose to tie up with. This integration allows them to offer products and services on their own rather than through licensed banks. This can reduce costs and increase profitability. Monzo Bank, NuBank, We Bank, and N26 are some known examples.
Over The Top
Technology companies partner with banks to provide tools, and completely digitize and automate different processes involved in the banking sector like onboarding of customers and account opening, transactional services like paying utility bills, insurance premiums, etc. Since it is a partnership model, the regulatory compliance will be looked after by the partner bank. This model lets fintech companies understand the existing loopholes of legacy banking and resolve it. These are digital-only platforms that don't have their own banking licenses. They offer either a stand-alone product or a set of financial products in partnership with financial institutions/banks and Fintech firms but at a lower cost as compared to traditional banks. Few even act as marketplaces for financial products via APIs. Examples are Open, Chime, Tide, and Varo.
An Initiative by Banks
Banks that realize the needs of the customer and understand the need for technological advancement. Few banks have started the digital-only initiatives where they have implemented standalone neobanks offering cutting-edge technologies and innovative use cases to drive the GenZ customers as well as retain the existing customer base. These digital banks use completely different digital financial services platforms as compared to their parent bank and target tech-savvy millennial customers by providing best-in-class innovative services. For instance, Digibank by DBS, Yono Bank by SBI, and Hello Bank by BNP Paribas.
Hybrid Model
In this model, a company might have a full fledge virtual banking license in few regions while working in partnership with existing banks in other areas where the virtual banking license provision is not available or cannot be acquired due to required limitations like legal requirements, approval for deal management within a country by a foreign country. Revolut for business is currently being used by over 20,000 businesses across the globe by adopting this hybrid model.
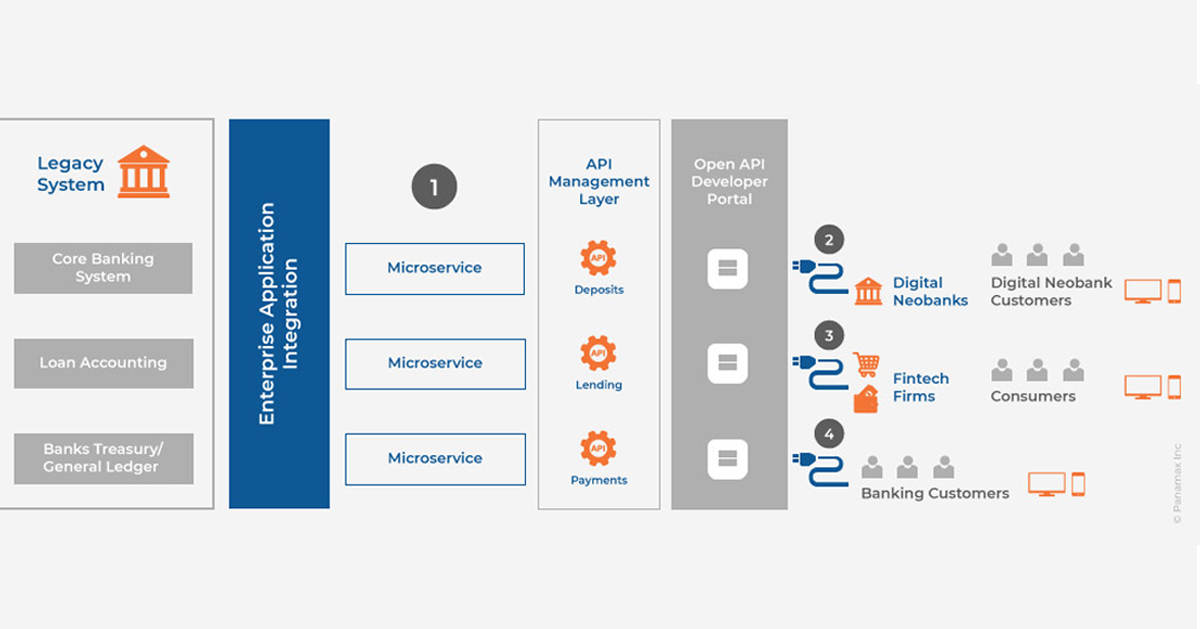
Building a Neobank
A Neobank can be built by developing the banking infrastructure using APIs (Application Programming Interface). APIs can be visualized as the building block to form the core banking framework. Further customization can lead to innovative use cases. Web services, microservices, and APIs together enable modernization of legacy systems by unifying them with a decoupled integration layer, bridging traditional batch-based processes with real-time, digital cloud, mobile, and social applications. APIs enable the modular application stack underlying Banking as a Platform (BaaP) and provide Neobanks with state-of-the-art digital banking capabilities.
- Integration APIs for Service Providers
- Banking APIs for Bank related services
- Innovation APIs from Fintech
- Connectivity APIs for Bank Customers
Neobank – Path towards Ultimate Digital Transformation of Banks
Collaboration is the key to the future. Open architecture is the next step towards the growth of the banks, insurers, and other Finserv. Neobank is a solution to achieving this goal. As the banking industry goes through a period of digital transformation, banks must take the full benefit of the technology providers for greater personalization, scalability, and be more customer-driven and platform-oriented.